Horn Shark
Heterodontus francisci
The horn shark, or Heterodontus francisci, is a smallish shark who likes warm shallower water but will go to depths of about 150 - 200m. They're mostly found in depths of 2 to 11m.

|
They're nocturnal and generally spend their days resting up in their
favourite little hidey hole somewhere on the seabed. Sounds like my kind
of life, though I think I'd prefer the beach to the seabed:) |
|
Size
On hatching the pups are about 15 cm long. At maturity the female is typically larger than the male. They usually grow to about a metre long with a maximum total length of about 122cm.
Colouring
These are pretty sharks (yes, even the boys) with a light greyish to brown body with small dark spots. There is a darker patch of tiny spots under each eye.
The colouring of the juvenile tends to be brighter than that of the adult. This may have to do with camouflage as the young horn sharks prefer to spend their days on the sandy seabed while adults are happier in rocky areas.
Fins
They have two dorsal fins and both have fin spines. These are mildly poisonous and can inflict a painful wound. They're used for defence.
Although they have large and mobile pectoral fins they are sluggish and clumsy swimmers. They often use their fins to crawl over the seabed. They have a pair of pelvic fins and an anal fin. The caudal fin is asymmetric with a notch in the longer upper lobe.
Teeth
The front teeth are small and pointy. These are used to grip prey while the powerful, flat, molar-like back teeth crush and grind it. Though they have a small mouth they have the most powerful recorded bite force in relation to its size of any species of shark.
Diet
Horn sharks suck. No, really, they do. They are able to form a tube with their mouth and expand the buccal cavity to literally use suction to capture their prey.
Juveniles prefer a softer diet to the adults and favour polychaete worms and sea anemones. Adults like molluscs, sea urchins and other benthic invertebrates.
Reproduction
These sharks are oviparous. Mating takes place in December and January with eggs being laid in February to April. Egg cases are spiral shaped and take approximately 7 to 9 months to hatch.
Although no shark species give any parental care, this female does pick up her eggs after laying then and wedge them into crevices on the rocky seabed to keep them as safe as possible.
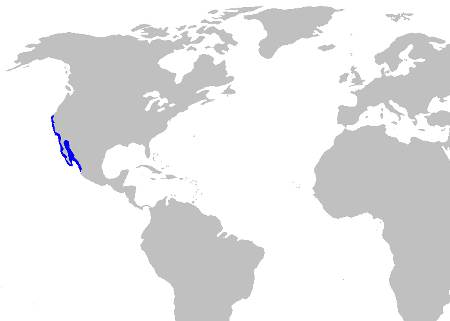
Distribution
This shark is found off the coast of America in the Eastern Pacific. They tend to stick to the same small areas where they shelter during the day and hunt at night.
Horn Shark Distribution Map
Return to Heterodontidae from Horn Shark
Classification
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Chondrichthyes
Subclass: Elsamobranchii
Order:Heterodontiformes
Family: Heterodontidae
Genus: Heterodontus
Species: francisci

Adult Head

Juvenile
Recent Articles
-
Thresher Sharks
Aug 27, 14 10:51 AM
Thresher sharks are unmistakable with that huge upper lobe on the caudal fin. Let's find out more about them. -
Sharkwater
Aug 14, 14 12:42 PM
Sharkwater is a documentary by Rob Stewart highlighting the plight of the sharks in our oceans. -
Natural Cleaners
Aug 13, 14 08:57 AM
Natural cleaners and homemade skincare products are not only better for the environment, they're better for you and your family.
